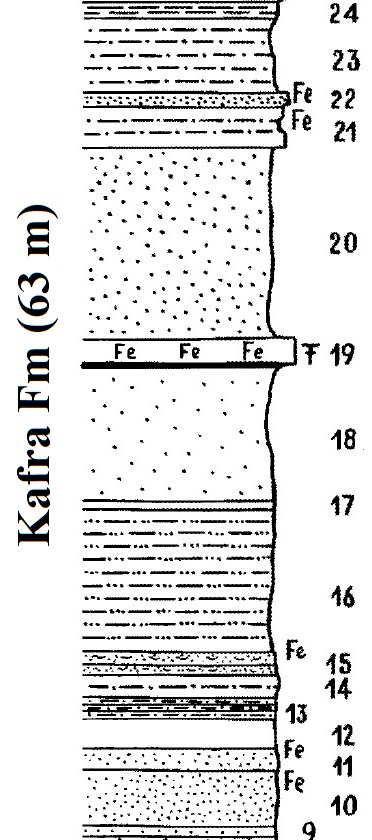
Kafra Fm
Type Locality and Naming
Oasis of Kafra. Faure, 1966.
References: Faure, 1966; Fabre et al., 1983.
Equivalent(s): Séguédine Fm; Agadem Fm
Lithology and Thickness
Kaolinic clays with ferruginous particles, with increasingly thicker sandstone levels towards the top. Faure (1966) describes the following section (see Figure):
- 24- (1 m) - There are numerous ferruginous platelets of shaly siltstone, red, soft or hard.
- 23- (6 m) - Very fine sandstone, white shale, finely sandy, variegated beds (ferruginous scree).
- 22- (1 m) - Ferruginous brown sandstone.
- 21- (3 m) - Depending on the beds, white clay sandstone, with ferruginous levels.
- 20- (15 m) - Fine sandstone, beige-brown, ferruginous at the top.
- 19- (1.8 m) - Large fossil-bearing ferruginous slab, forming a corniche.
- 18- (10 m) - Very fine sandstone, bedded, variegated, lace area towards the top. Purple, red, white.
- 17- (0.5 m) - Very fine shaly white level, locally zoned.
- 16- (11 m) - Shale finely sandy (hidden by scree of large ferruginous slabs).
- 15- (2 m) - Ferruginous slab with traces of fossils
- 14- (1 m) - White beige sandstone with thin shaly joints and clay nodules of 1 cm at the base.
- 13- (2.5 m) - Alternating eight beds of white to yellow sandstone (15 c m) and grayish shale (10 c m) in joints.
- 12- (2 m) - Hidden.
- 11- (4 m) - Homogeneous fine sandstone, khaki brown, with scoriaceous ferruginous slabs.
- 10- (2 m) - Fine sandstone, hidden.
- 09- (0.5 m) - Fine yellow sandstone.
Total Thickness: ~63 m
[Figure. Section of the Kafra Fm at the water wells of Kafra (Source: Faure, 1966, p. 235).]
Relationships and Distribution
Lower contact
Underlying unit is the Zoo Baba Fm
Upper contact
Overlain by the Bilma Fm
Regional extent
East Niger Rift Basin - Bilma Sub-basin - South
GeoJSON
Fossils
Plant imprints are pretty frequent. Lamellibranchs of the “Cameroonian” type
Age
Depositional setting
Marine and continental origin
Additional Information